Question
With reference to the corrosion of metals,
write notes on electrolytic corrosion the precaution necessary when using
(i)
Aluminium and steel in the same compartment, (ii)
ammonia.
Answer.
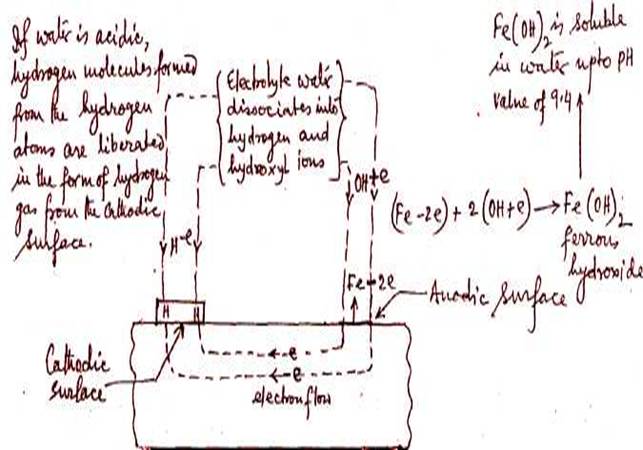
a. Electrolytic corrosion is encountered as a result
of reaction of metals with water containing hydrogen ions and involves a
transfer of electrons. A flow of electricity between certain areas of the metal
to other areas takes place through the water as electrolyte due to difference
of potential.
The hydrogen
ions in water, in contact with the metal surface become hydrogen atoms by
taking an electron from the metal. The resultant metal ion (caused through loss
of electron ) combines with the hydroxyl ions in
contact with the metal surface to form a metallic hydroxide, which is soluble
in the water depending on the pH valve, hence the metal is corroded.
Hydrogen, which has formed on the surface of the metal
due to the combination of the hydrogen ion and metal electron
may form a polarizing layer upon the metal surface. This will prevent further
corrosion. If however, dissolved oxygen is present in the water, it will
combine with the hydrogen to form water and no polarisation
will occur and corrosion will continue. Also if the water is acidic enough, the
hydrogen can leave the surface of metal in the form of hydrogen gas, again
preventing polarization and continuing corrosion. Thus the
need for water to be alkaline and with little or no dissolved oxygen content to
prevent electrolytic corrosion.
(b) (i)
Bimetallic corrosion due to galvanic action occurs when two dissimilar metals,
e.g. aluminium and steel are in direct contact with
each other or indirectly through an electrolyte. To prevent corrosion, the
metals must be insulated from each other or protected by a good paint film.
More noble metal steel in the galvanic series acts as cathode and less noble
metal aluminium acts as anode and corrodes. The more
noble metal steel must be used for fasteners to join the two metals.
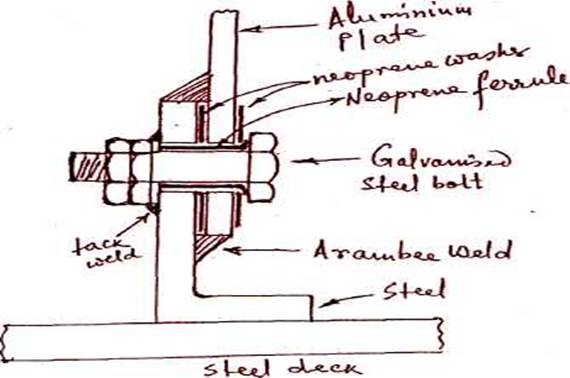
The contact between the two metals is prevented by using neoprene washers and neoprene ferrule. Galvanised steel bolts are used and the nuts are fitted in the inside of the house and tack welded to boundary angle to allow the joint to be tightened without removal of the internal linings. The top and bottom of the joints are specially welded with a compound known as arambee to form a watertight seal.