Question.
Describe the DB and framing arrangement used
in the machinery space to cope with concentrated loads and vibration together
with shaft and thrust block support
Give reason for choice of thrust block
position
Answer.
Double bottom in the machinery space
In the machinery space other factors must be taken
into account. Forces of pulsating nature are transmitted through the structure
due to the general out of balance forces of the machinery parts. The machinery
seats must be extremely well supported to prevent any movement of the
machinery. Additional girders are fitted in the double bottom and the thickness
of the tank top increased under the engine in an attempt to reduce the
possibility of movement which could cause severe vibration in the ship. For
similar reasons the shaft and propeller must be well supported.
Great care must be taken in the machinery space to
ensure that the main and auxiliary machinery are efficiently supported. Weak
supports may cause damage to the machinery, while large unsupported panels of
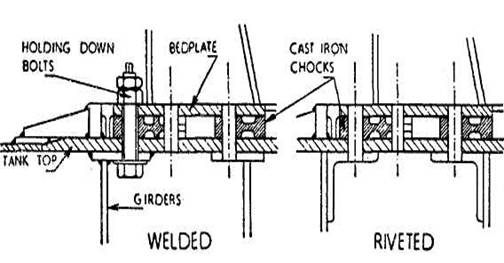
plating may lead to vibration of the structure. The main engine bedplate is
bolted through a tank top plate which is about 40 mm thick and is continuous to
the thrust block seating. A girder is fitted on each side of the bedplate in
such a way that the holding down bolts pass through the top angle of the
girder. In welded ships a horizontal flat is sometimes fitted to the top of the
girder in way of the holding-down bolts.
In motor ships where a drain tank is required under the
machinery, a cofferdam is fitted giving access to the holding down bolts and
isolating the drain from the remainder of the double bottom tanks. Additional
longitudinal girders are fitted in way of heavy auxiliary machinery such as
generators.
Thrust Block Position & Support:-
Main thrust block is placed closed to the propulsion
machinery in order to reduce any problem due to differential expansion of the
shaft and the hull. The low hull temperature of midship
engined refrigerated cargo ships can cause a
contraction of upto 20mm relative to the shaft
whereas water temp, change or heating of fuel tanks can cause expansion of
hull. Other problems include whirling of tail shaft, relative movement of the
hull and misalignment due to droop from propeller weights. Deformation produced
by the thrust load can cause misalignment problems, unless suitable stiffening
is employed (particularly with an end of gearbox installation).
Support :-
The substantial double-bottom structure under the main machinery provides an ideal foundation for the thrust block and is the reason for siting the thrust block close to the engine. The upright thrust block and any supporting stool must have adequate strength to with stand the effect of loading which tends to cause a forward tilt. This results in lift of aft journal of the block and misalignment of the shaft. Axial vibration of the shaft system, caused by slackening of propeller blade load as it turns in the sternframe or by the play of diesel engine crankwebs, is normally damped by the thrust block. Serious vibration problems sometimes cause thrust block to rock, panting of the tanktop and structural damage.