Question
Sketch a cross section of a bulk carrier
with either deep or shallow D.B. showing the types of framing used
Describe the corrosion problem experienced
with ballast tanks
State how such tanks are protected against
corrosion.
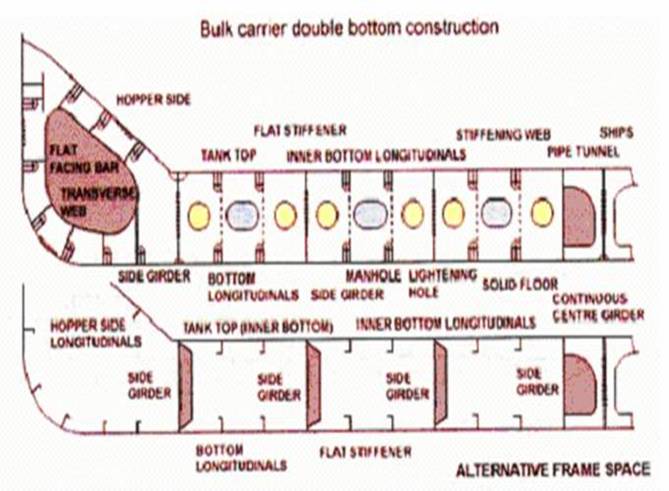
With the reduction in the number of new ships built,
the older vessels in service have extended lives and these have shown some
severe corrosion problems in ballast tanks. The problems are made
worse by the neglect of maintenance and the use of thinner^ scantling when high
tensile steel is used. The most serious problems ha^.e been found in permanent ballast tanks.
Galvanic corrosion can rapidly eat into the structure and rates increase with
temperature and differential aeration (bottom of the tank is lower in oxygen
concentration and hence anodic to die top).
The presence of sulphate
reducing bacteria, cause further microbiological degradation.
The muds of some river beds
are particularly rich in SRB. The bacteria can cause local pitting which has
been known to penetrate the bottom shell.
Protection of ballast tanks is by complete paint
coatings supplemented by sacrificial anodes. Some older ships have main anodes
and booster anodes. The booster anode have large
surface area to volume ratio (flat discs) causing rapid cation
formation at cathode (steelwork) which cleans the surface of rust and
scale. A protective film is 'formed but this can quickly be removed in
surface therefore a main anode which has a large volume to surface area ratio
(hemispherical) are fitted and should last about 3
years.
Hydrogen gas is formed on the cathode (steelwork) of
the tanks, hence the tanks should be pressed up to
prevent the formation of hydrogen gas pockets in the vapour
space of slack tanks. The tank venting system should be operational
when emptying the ballast tank with precautions taken as for a low flash point
cargo. The tank should be considered non gas
free until tested.
Ballast tanks that have been empty for some time may
have atmospheres deficient in oxygen which is consumed in the corrosion
process. Deaths of crew entering such spaces have occurred (see
M.910) therefore the tank must be fully vented before entering and 'Entry to
enclosed spaces' procedures
observed.
Maintenance includes cleaning and re-coating with pits
filled or welded: Serious corrosion over an extensive area would
need plate renewal.