Question
What is The Effect of wind
and waves
When a ship
is inclined by an external force, such as wind and wave action, the centre of
buoyancy moves out to the low side, parallel to the shift of the centre of
gravity of the immersed and emerged wedges, to the new centre of gravity of the
underwater volume. The force of buoyancy is
considered to act vertically upwards through the centre of buoyancy, whilst the
weight of the ship is considered to act vertically downwards through the centre
of gravity. These two equal and opposite forces produce a moment or couple which
may tend to right or capsize the ship. The moment is referred to as the moment
of statical stability and may be defined as the
moment to return the ship to the initial position when inclined by an external
force.
Question
What is The Effect of trim
on tank sounding.
A tank sounding pipe is
usually situated at the after end of the tank and will therefore only indicate
the depth of the liquid at that end of the tank, if a ship is trimmed by the
stern, the sounding obtained will indicate a greater depth of liquid than is
actually contained in the tank. For this reason it is desirable to find the
head of liquid required in the sounding pipe which will indicate that the tank
is full.
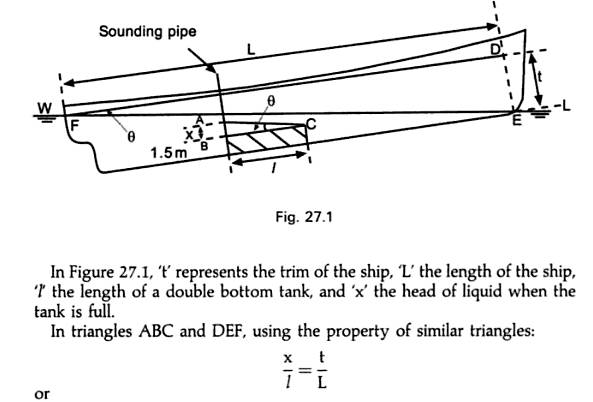
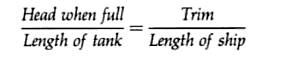
Trim may be considered as
the longitudinal equivalent of list.
Trim is also known as
longitudinal stability. It is in effect transverse stability turned through
90°.
Instead of trim being
measured in degrees it is measured as the difference between the drafts forward
and aft. If difference is zero then the ship is on even keel. If forward draft
is greater than aft draft, the vessel is trimming by the bow. If aft draft is
greater than the forward draft, the vessel is trimming by the stern.
Question
What is Reserve Buoyancy?
When a
floating vessel displace its own weight of water.
It is the submerged portion of a floating
vessel which provides the buoyancy.
The volume
of the enclosed spaces above the water line are not providing buoyancy
but are being held in reserve. If extra weights are loaded to increase the
displacement, these spaces above the waterline are there to provide the extra
buoyancy required.
Thus, reserve buoyancy may
be defined as the volume of the enclosed spaces above the waterline. It may be expressed
as a volume or as a percentage of the total volume of the vessel.