Question
Describe a circuit breaker for a a.c.
generator using sketch to show how arcing is controlled
Explain the sequence of event that might occur if the breaker
opens on a short circuit and state the check you would require following such
event
Give a safe procedure to follow should a main circuit breaker
fails to open under fault condition.
Answer.
Sketch.
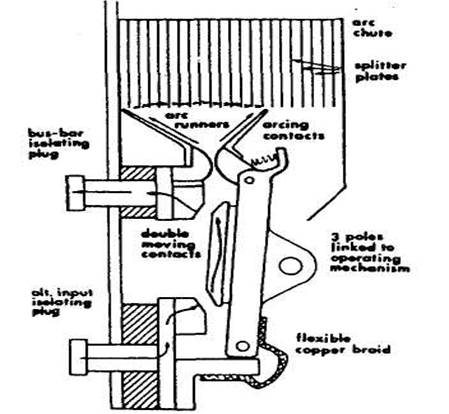
Alternator circuit
breakers
The air-break circuit breakers used for marine installations
are frame-mounted and arranged for isolation from busbar
and alternator input cable contacts by being moved horizontally forward to a
fixed position. The isolating plugs (Figure) are not designed for making or
breaking contact on load so the breaker must be open before the assembly is
withdrawn.
The alternator breaker for three-phase supply has a single
unit for each phase, of similar design to the example in Figure.
The three units are linked together by an insulated bar for
simultaneous operation.
Main fixed and moving contacts are constructed of
high-conductivity copper, and as an aid to low contact resistance the faces are
silver plated.
Main contacts are designed to carry normal full load current
without overheating and overload current until tripped, when a fault occurs.
Interruption of current flow results in the production of an
arc between contact faces.
Arcing is severe with overload current but is not a serious
problem during normal operation.
To prevent damage to main contacts, separate arcing contacts
are fitted which are designed to open after and close before main contacts.
These supplementary contacts are of arc-resisting alloy such
as silver tungsten and easily replaced if damaged.
The arcing contact shown has a spring which pushes it forward
to hold until after main contacts have opened.
Arc control requires that the arc be elongated and removed
from the gap between the arcing contacts. Electromagnetic forces associated
with the arc and thermal action cause it to move up
the arc runners to the arc chute provided for the purpose.
Thus the arc is elongated and finally chopped into sections
and cooled by the splitter plates.
Arc chutes are of insulating and arc-resisting material.
They confine the arc and produce a funnel effect which
assists thermal action.
Splitter plates are of metal (steel or copper) in some
breakers, and in others of insulator material.
Interruption of the arc is assisted by the current dropping
to zero during the cycle (however, with three-phases the zero points in each
phase are staggered).
Contact opening is therefore followed by a current zero and
this means that for the next part of the cycle, an arc has to be struck across
a gap.
Successful removal of ionised gas (from the arc which
resulted from contact opening) will increase resistance in the air gap between
contacts. When gas remains, it provides a path across which the arc can
re-strike.
The rate at which the gas is removed is such that the arc
will not re-strike more than two or three times.
Breaking speed is made as high as possible by powerful
throw-off springs and light construction of the moving arm assembly. Rebound at
the end of the opening movement is prevented by anti-bounce devices.
The alternator breaker has an over current trip but the major
consideration is that
The alternator breaker has an over current trip, but a major
consideration is that the supply of power to the switchboard must be maintained
if possible.
The breaker therefore is arranged to be tripped instantly
only in the event of high over current such as that associated with short
circuit.
When over current is not so high, a delay with inverse time
characteristic allows an interval before the breaker is opened. During this
time the overload may be cleared.
Straight overload (apart from the brief overload due to
starting of motors) is reduced by the preference trips which are designed to
shed non-essential switchboard load.
Preference trips are operated by relays set at about 110% of
normal full load.
They open the breakers feeding ventilation fans, air
conditioning equipment etc.
The non-essential items are disconnected at timed intervals,
so reducing alternator load.
A serious fault on the distribution side of the switchboard
should cause the appropriate supply breaker to open, or fuse to operate, due to
over current. Disconnection of faulty equipment will reduce alternator
overload.
After a short circuit trip the breaker should be
Inspected for possible damage to contacts
The close trip mechanism operated and checked
Insulation reading between poles and each pole to earth
should be taken
A minimum of 5 m-ohm is usually specified
by the manufactures
If the main circuit breaker fails under fault condition
Start another generator and take it on load
Shift maximum load on this generator
When the load on the faulty generator is very low then trip
the breaker manually