Tank liquid sensors are an
integral part of the ship
Describe with the aid of
suitable sketches the working principle of cap activity type level sensor
Ultra level sensor
Float.
Level Detection and Measurement by Using a
Float Sensor
Level Detection Using a Float Sensor
Principle of Operation: A liquid level control system by
using a float sensor works on the principle of buoyancy, which states, “A float
immersed in a liquid is buoyed towards upward direction by an applied equal
force to the weight of the displaced liquid”. As a result, the body drives
partially and gets submerged upon the liquid surface and covers the same
distance the liquid level moves.
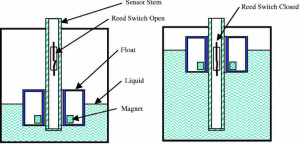
Construction: A level measurement float system
consists of a float, a sensor stem, a magnet, a reed
switch and a weight suspended on the outside of the open tank. A scale is fixed
on the outside of the tank, and the contents of the tank’s level are indicated
by the position of the weight along the scale.
Working: Level detection of liquids is often
done with a float-type
liquid level switch. The float transfers on a mechanical arm or
sliding pole and activates a switch when the level moves towards upward
direction. Sometimes the float itself contains a small magnet that
varies the state of a switch when the liquid level gets moving up and moves
into the original position. This type of level sensor comes with many advantages
like it is very simple, highly accurate, and best suitable for various products.
The
Disadvantages of this sensor are that it requires various
mechanical equipment, especially the pressure vessels.
Primary Areas of Float Sensor
Application: In view of the requirements
pertaining to the increase in usage of sealed tanks, the current industrial
systems make use of this type of float method for precise reading and
accuracy, which is a good example of electronics and mechanical engineering,
making it the most accurate level-measuring system for various applications in
very large storage tanks.
2. Level Detection and Measurement by Using
Capacitance Sensor
Level Detection Using Capacitance
Sensor
Capacitance
level sensors are made available for wide range of solids, aqueous, organic
liquids and slurries. This technique is frequently stated as the
radio-frequency signals applied to a capacitance circuit. The capacitive
sensors are designed to sense material with dielectric constants as low as 1.1
for coke and fly ash, and as high as 88 for water or other liquids.
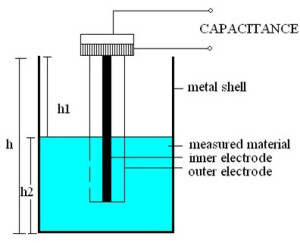
Principle of operation: The principle of capacitive level
measurement is based on the change of capacitance. There are two plates in
capacitive sensor: one plate acts as an insulated electrode and the other plate
acts as a tank wall. The capacitance depends on the liquid level. An empty tank
has low capacitance while a filled tank has higher capacitance. A simple
capacitor consists of two electrode plates separated by a small thickness of an
insulator such as solid, fluid, gas, or vacuum.
The Value of C
depends on dielectric constant used, area of the plate and also on the distance
between the plates.
C=E(KA/d) Where: C = Capacitance in Pico farads (pF) E = a constant known as the absolute permittivity of
free space K = Relative dielectric constant of the insulating material A = Effective
area of the conductors d = Distance between the conductors
This change in capacitance can be
measured by using an AC Bridge.
Construction and Working
The measurement
of liquid level is done by applying a Radio Frequency signal between the
conductive probe and the vessel wall. The Radio Frequency signal results
in a very-low current which flows through the dielectric process material in
the tank from the probe to the vessel wall. If the liquid level in the tank
drops, then the dielectric constant decreases, which leads to the drop in
capacitance reading as well as minute drop in current flow.
This change can
be detected by the liquid-level switch’s internal circuitry and translated into
relay state changes of the level switch in case of a point level detection.
The main
advantages of these capacitance systems include easy installation, broad
application range, good accuracy suitable for variety of applications and
highly recognized and well -proven technology.
The
disadvantages include sensitivity to changes in the measurable properties such
as dielectric constant and conductivity which creates an issue; furthermore, it
is an intrusive system.
Primary
Areas of Capacitance Sensor Application: Capacitance level sensor probes are
used for measuring the levels of:
- Fluids
- Liquid metals
at very-high temperature range
- Dissolved
gases at very-low level of temperature
- Very-high
density industrial processes.
Continuous Level Measurement and Detection
Systems
A continuous
level sensor is most sophisticated and also provides liquid level monitoring of
an entire system. This liquid level sensor is used to measure the fluid level
within a specified range, moderately than at a one point, which produces an
analog output and directly correlates to the level in the vessel. To create a
liquid level management system, the output signal is interconnected to process
a control loop and linked as a visual liquid level indicator. This measurement
system consists of variety of sensors such as
- Ultrasonic
Sensor
1. Level Detection and Measurement by Using
Ultrasonic Sensor
Level Detection Using Ultrasonic
Sensor
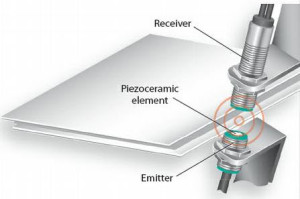
Ultrasonic level
instruments works on the basic time-of-flight principle which states that
sending a sound wave from a peizo electric transducer
to the contents of the vessel, which may contain liquid, solid or slurries
level.
This liquid
level sensor comprises two elements such as an associated electronic
transceiver and a transducer with relatively high efficiency. In case of a liquid level controller, the fluid
level can be determined by measuring the trip time difference between a
transmitted ultrasonic pulse and a reflected echo.
The frequency
range for ultrasonic methods varies from a range of 15-200 kHz for transmitting
and receiving ultrasonic waves. The lower frequency instruments are used for
the measurement of difficult applications such as longer distances and
solid-level measurements, and the instruments with higher frequency are used
for shorter liquid level measurements.
The ultrasonic
sensors are advantageous as they are not in direct contact with the product,
and the level measurement is done without involving any physical contact. They
do not have any moving parts.
As a
disadvantage, these types of sensors are not suitable for higher pressures in a
vacuum and temperature limits of up to 170 degree centigrade.