Question
With reference to fire detection
unit
Describe a rate of heat rise detector
with the aid of a sketch.
Describe the following methods of
checking the integrity of a suction of fire detection heads
Loop monitoring.
Line
termination monitoring.
Bimetal strips made up from brass
and INVAR will deflect when heated due to the high expansion coefficient of the
brass and the low expansion coefficient of the INVAR, which is 36% nickel steel
Deflection increases with temperature and could in itself be used to complete
an electrical circuit and operate an alarm at some specific figure. However,
rate of rise can be detected using two bimetal strips (Figure) of different
thickness.
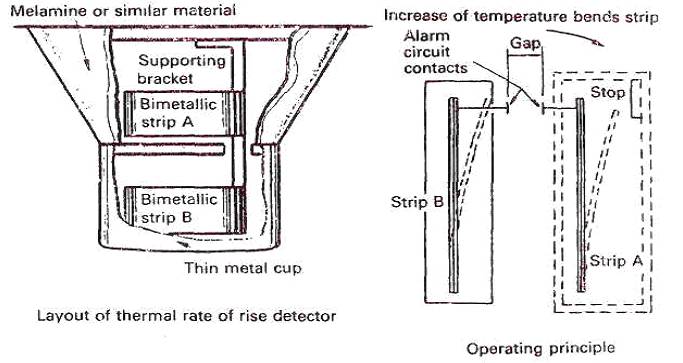
Figure
These are set up parallel to each
other and arranged to deflect in the same direction. Rapid temperature rise
will cause the thinner element to deflect more quickly than the other, so
causing contact to be made and the alarm circuit to be completed. A slow rise
causes a similar deflection in both elements, so that a gap between the
contacts persists, until a certain maximum temperature if reached when contact
is made because of other differences in the make up of the strips.
Loop monitoring.
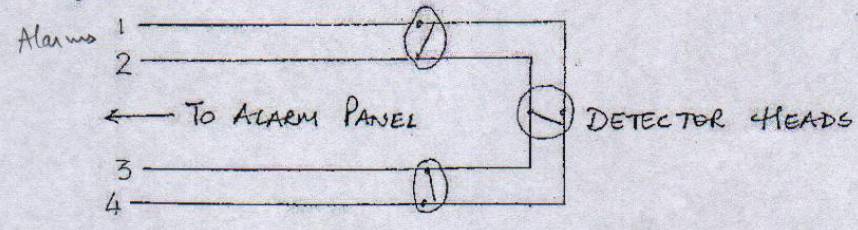
The alarms are activated by the
closure of the contacts in the heads through 1 and 2
While continuity
is checked through 1 and 4 and 2 & 3.
Line
termination monitoring.

The alarms operate when contact
across 1 & 2 close. Continuity is checked by monitoring the resistance at
the end of the line.
If the resistance of the line
measured across 1 and 2 is less than the end resistance the alarm sounds
If the resistance of the line
measured across 1 and 2 is greater than the end resistance plus the cable resistance
a system fault alarm is activated.