Question
Explain meaning with reference to
electrical safety equipment.
Intrinsically safe
An intrinsically safe circuit is
one that is designed for a power so low that any spark or thermal effect
produced by it, whether there is a fault or not, is incapable of igniting the
surrounding flammable gas or vapour. It follows that intrinsically safe
equipment is used in such circuits and is designed on the same basis, i.e. of
being unable to produce a spark with enough power to ignite the specific
flammable vapour or gas involved. Intrinsic safety technique requires not only
that a system is designed for operation with very low power, but also that it
is made invulnerable to high external energies and other effects.
Flame proof
Flameproof enclosures are used for equipment
where sparking or arcing occurs during normal operation, as in a switch or starter.
The spark is contained and likewise any flame or explosion (of gas which might enter
the casing), preventing ignition of a surrounding explosive atmosphere.
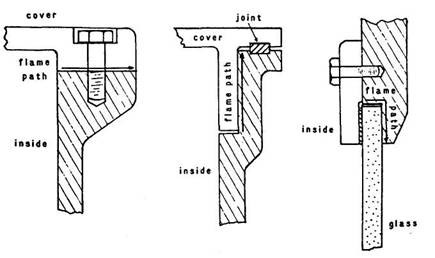
Figure Flame paths in Ex d equipment
Flameproof Ex d protection can be
applied to any type of rotating electrical machine but is intended for those
where the ignition of a flammable atmosphere is likely because sparks or arcing
occur during normal operation of the machine. Wound rotor induction motors with
slip-rings and brushes, also commutator motors, are,
because of sparking, likely to be protected by a flameproof (Ex d) enclosure.
With such protection, a particular piece of equipment may be acceptable for
zone 1 and zone 2 areas but the flameproof protection does not make it suitable
for the most hazardous zone 0 locations.
Increased
safety.
Increased safety (Ex e) equipment
A squirrel-cage induction motor is
a type of electrical apparatus which does not normally have any associated
arcing or sparking during operation and where running temperature is not
excessive. Such equipment can be made safe for operation in areas made
hazardous by the likelihood of flammable vapour, by the use of increased safety
techniques.
Insulation for windings and cables
is of high quality and protection is given against ingress of water or solids
which could cause insulation breakdown. Breakdown of insulation due to
overheating from overload is prevented by overload devices, which are an
essential part of the increased safety technique. Adequate clearance is given
to the fan and rotor to avoid mechanical sparks from rubbing contact and the
casing is made impact-resistant. Power supply terminals are of non-loosening
type and well separated to prevent tracking and the cables are firmly
supported. The overload devices which protect the insulation also prevent
excessive external or internal temperature.
Pressurised (Ex p) equipment
Some deck lights used for tankers
are operated by compressed air turbines which drive small individual generators
within the fitting to provide power for the lamp. The exhaust air pressurises
and purges the fitting, so excluding any flammable gas which might be present
in the external atmosphere. Failure of the air supply automatically causes the power
to be switched off.
The technique of pressurising is
also used in straightforward types of electrical apparatus, particularly where
it is necessary to install a non-standard piece of equipment in a hazardous
area. Ex p equipment is not permitted to be installed in very hazardous areas.
Alarms and automatic shutdown at loss of pressurisation are required if
normally sparking Ex p type apparatus is installed
where a flammable atmosphere is likely to occur.
Pressurisation has been used for
control cabinets and enclosed spaces for' safe containment of sparking
electrical equipment. All pressurised spaces must be thoroughly purged before
the equipment is switched on.
Sketch a safety barrier for intrinsically
safe circuit
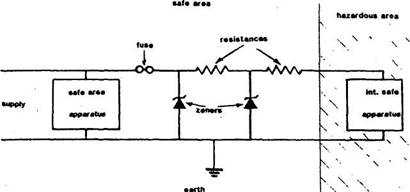
Figure .4 Safety barrier
for Ex i equipment
The purpose of such a barrier is to
limit voltage and current in hazardous area when fault occurs.
Fuse to limit maximum current
through zener diodes.
Resistors
to limit maximum current in hazardous area.
Zenor diodes to limit maximum voltage
with hazardous areas.