Question
Describe the devices used to
protect a 3 phase a.c. induction motor against the
following faults.
Short circuit
Overload
Single phase
fault.
Explain in contest of 1 & 2 why
discrimination is necessary.
If a
short-circuit occurs in the motor, the starter, or the supply cable,
then a huge fault current will flow.
If the contactor tries to open
under short-circuit conditions, serious arcing will occur at its contacts such
that it may fail to interrupt the fault current.
The prolonged short-circuit current
will cause serious damage to the motor, starter and cable with the attendant
risk of an electrical fire.
To prevent this, a set of fuses or
a circuit breaker is fitted upstream of the contactor which will trip out
almost instantaneously thereby protecting the contactor during a short-circuit
fault.
Overload
The thermistor
sensor is probably the most common as its thermal characteristic more closely
matches that of a motor than the other types.
Thermistors are small
pellets of semiconductor material which are embedded into the insulation of all
three motor stator windings during manufacture.
When a thermistor gets hot its resistance changes dramatically.
They are connected so that if the
motor temperature gets too high the starter contactor will be tripped by an
electronic protection relay to stop the motor.
Direct thermistor
protection is usually only fitted to large motors, e.g. bow thrusters, FD fans,
air conditioning compressors, etc.
Most motors are protected by
monitoring the temperature indirectly by measuring the current flowing in the
supply lines.
This method uses electronic,
thermal or electromagnetic time-delayed overcurrent relays
(OCRs) in the motor starter.
The system is designed so that if
the motor takes too much current because it is mechanically overloaded, the OCR
will trip out the contactor coil, after a pre-set time delay, before severe
overheating can occur.
The largest overcurrent
possible is the current taken when the motor has stalled.
This, of course, is the starting
current of the motor which will be about five times the full load current. The
contactor is capable of tripping this stalled current quickly and safely.
To operate correctly, induction
motors must be connected to a three phase a.c.
supply.
Once
started they may continue to run even if one of the three supply lines becomes
disconnected.
This is called single-phasing and
can result in motor burn-out.
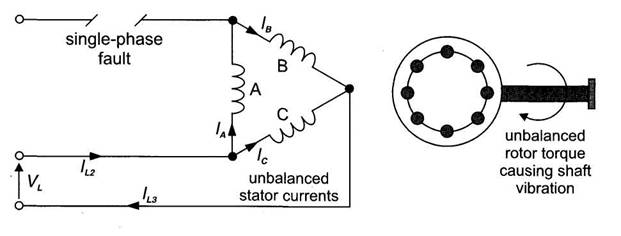
Fig. Single-phasing fault.
Single-phasing, as shown in Fig.,
is usually caused when one of the three back-up fuses blows or if one of the
contactor contacts is open-circuited.
The effect of single-phasing is to
increase the current in the two remaining lines and cause the motor to become
very noisy due to the uneven torque produced in the rotor.
An increase in line current due to
single-phasing will be detected by the protective OCR.
The three thermal elements of an
OCR are arranged in such a way that unequal heating of the bi-metal strips
causes a differential movement which operates the OCR switch contacts to trip
out the motor contactor.
