Question
In a A.C.
generator voltage dip occurs in 2 stages
Sketch a voltage time graph showing
the pattern of voltage dip
Referring
to this graph state with reason the effect on the electrical system of a small
power installation when large load is suddenly switched on.
Explain each of the following
categories of voltage control.
Error operated.
Functional.
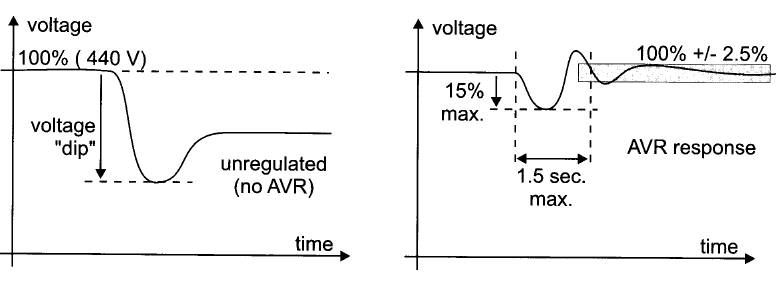
The voltage of an unregulated a.c. generator can vary 30% or more from no load to full
load, when sudden load is connected. The out put voltage changes, due to
internal voltage dip in generator winding.
In a regulated AVR. AVR
will control the generator's voltage to ±2.5% (or better) of its set value over
the full load range. This is its steady-state voltage regulation.
Transient voltage dip is usually limited to
15% for a specified sudden load change with recovery back to rated voltage
within 1.5 seconds because AVR increases the field current to restore voltage.
The voltage dip can cause light to
dim and may affect electronic equipment
Can slow down or stall the running
motor and affect the under voltage devices.
Error operated.
Measures output voltage and compares to
reference.
The function of error operated type
AVR is to maintain the terminal voltage of the generator within acceptable limit
under steady load and transient load condition
Functional.
The load current causes the voltage
to change
The load current is used to alter
the excitation as load increases.