COMBUSTION OF FUEL :
A general indication of good combustion is clear exhaust, correct amount of power and normal exhaust temperature, no uneven running or knocking from cylinders.
Residual fuel is heated in the Settling Tank and sucked through Transfer Pump, Filter and purified and sent to Service Tank. Fuel from Service Tank is heated to correct viscosity and then goes to fuel pump.
The fuel pump plunger compresses the fuel, the compressed fuel creates a pressure wave (abot 1300 m/sec.) which runs through pipe and injector, causing the nozzle to open and inject. Before the fuel is pushed into the pressure pipe (linking the pump and fuel injector), it has to pass the pressure valve which has several tasks. The first task is to separate hydraulically the pump from the pressure pipe after the fuel has passed the pressure valve; the second is to smooth the pressure wave running back and forth within the pipe, this calming down is necessary to secure the proper closing of the fuel injector without having additional and uncontrolled injection; and the third is to maintain a certain pressure within the pressure pipe for the next injection stroke (rest pressure). The pressure valve is manufactured with tight tolerance to perform the task and -the pressure pipe has to withstand pressure waves upto 1800 bar at about 1300 m/sec. speed.
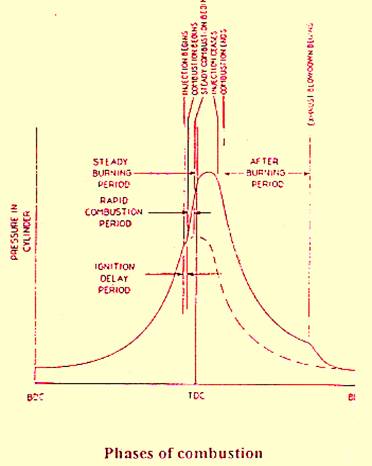
The atomised oil droplets" emitted from fuel injector nozzle having a high surface area goes into the combustion space, at the start of the injection will evaporate and mix with hot compressed air. The mixture will reach a high compression pressure and ignition temperature and spontaneous combustion will commence. The time elapsed during this fuel injection and combustion to start is termed the Ignition delay.
Cetane Index is an empirical measure of ignition, quality of distillate fuels. The index is calculated from the mid boiling point and density i.e. from parameters which relate indirectly to the chemical composition of the fuel. A high cetane number indicates a short ignition delay. Slow speed 2-strokes engines can operate efficiently on fuels down to cetane number of 24, but medium speed, 4-stroke engine normally require a figure above 34, high speed engines require higher cetane number.
For residual fuel, there are two empirical measures of ignition quality. In both equations, use is made of the density and viscosity parameters of the fuel. CCAI (Calculated Carbon Aromaxicity Index) or CII (Calculated Ignition Index) are the measure of ignition delay for residual fuels. Lower the CCAI value, the better the ignition quality i.e. less the ignition delay. Ignition quality is particularly important for ease of starting an engine or when operation at reduced power for long periods. It can be improved by advancing the timing, increasing the compression ratio or by pre-heating the scavenge air. However there are design or operational limits to these.
CCAI value ■= f - 81 - 141 log [log(V + 0.85)] - 483log[(T + 273)/323]
where f = density in Kg/m3 at 15°C.
V = Kinematic viscosity in CST
T = Temperature in °C at which viscosity is measured.

It appears that the value above which ignition problem are experienced can occur is in the range of 850-890.
After the initial ignition, combustion will set up a flame front which will accelerate through the chamber enveloping and burning all the droplets present, causing a very rapid generation of heat with corresponding rise in pressure and temperature. During the ignition delay, the injector continues to inject fuel and if this builds a sufficient quantity, the combustion and pressure rise will be quite violent, causing detonation, shock loading creating a noise termed Diesel Knock.
Following the rapid pressure rise, hot turbulent condition existing in the combustion chamber will cause the ignition and burning of the remainder of the fuel charges as it is injected. This is termed the controlled part of the combustion process, as pressure is regulated by the rate at which fuel continue to be delivered. This ends after the injector closes.
The cylinder pressure may start to reduce as the piston moves down after passing over top centre. The expansion stoke begins and pressure drops rapidly. This period is termed as afterburning period.